Fraud, abuse and waste represent key challenges for any Healthcare Insurer looking to address cost management. Such practices may be witnessed across the Health Insurance industry, from patients to healthcare providers and organisations. But observation cannot be passive: it must lead to action.
Fraudulent payments hit the bottom line of all stakeholders, public and private. As a consequence, it is essential that insurers implement a fraud control model: one that will apply in the treatment phase, but, critically, one that will also serve prevention and dissuasion purposes.
The main different types of fraud that insurers face
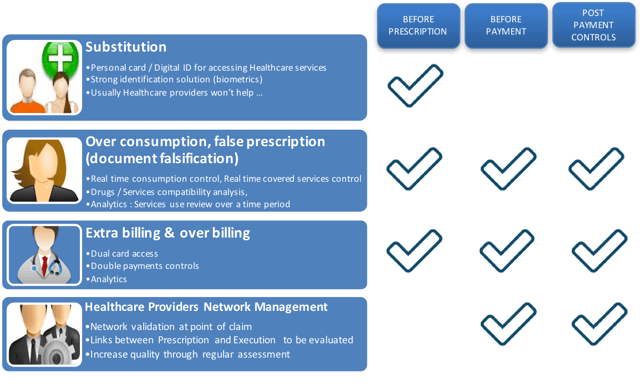
Insurers are confronted daily by four main types of fraud:
- Substitution or identity theft
- Over-consumption or false prescription
- Extra billing and over-billing
- False declarations by healthcare providers
The different models of fraud management
There are three major models to manage fraud:
- The curative model (the most common), consisting in post-payment controls, be these payments to patients or healthcare organisations. Its punitive measures range from penalties to money recall and contract cancellations.
- The preventive model, consisting in requesting detailed invoices and justifications before proceeding to payment. It requires regular communication to peers to prove effective.
- The dissuasive model, centred around increasing the burden of documentary proof in the reimbursement process. In addition to invoices and justifications, the insurer will request all exams results. Whilst very efficient, this strategy is seldom applied, as, with the burden of proof comes a heavy administrative burden in the shape of vast amounts of supportive documents to handle potentially hampering competitiveness.
The fraud prevention challenges
For treatment courses, the challenge is to store enough information, over a long period of time (usually five years in Europe), specifically to comply with the legal fraud management process. This data will be mainly linked to fraud qualification data and constitutive elements for fraud recovery.
For preventive actions, the challenge is to implement all the technological, regulatory and procedural tools that will ensure that the right patient receives the right treatment, at the right price, ensuring the system limits substitution, over-consumption and extra billing.
Finally, for dissuasive actions, the challenge is to manage the administrative burden and the storage of all related documentation.
How can Information Systems help prevent fraud?
An insurer’s Information System (or core solution) plays a key role in the efficient management of fraud. That’s why it must provide features capable of managing specific issues:
- Claims adjudication: a smart engine shall be able to detect any issues on the claims, through automation (eligibility check, control of duplicates, application of deductibles, application of limits…) and control of claim parameters (like history of patients and families), as well as control of complex claims.
- Pre-authorisation and case management: similarly, the core system has to ensure controls automation and real-time reconciliation between the pre-authorisation and the claim.
- Provider management and agreements: this requires the core system to have a flexible framework that can manage all contracts with different Healthcare professionals, and that can automatically manage cost and agreement controls (e.g. prices, discounts, control of commercial agreements at claim adjudication…).
- Compliance and risk audit: the core system has to handle high volumes of information, ensure data integrity (version management, control of duplicates, high security), manage risk and provide an audit trail (separation of duties, anti-money laundering checklist, claim investigation and recovery process support, comprehensive user auditing).
- Healthcare Professionals assessment: last but not least, to efficiently manage Healthcare Professionals Networks, the implementation of Trust scores will be key. The core system needs to integrate the capability to compute a real-time trust score.
To find out more about this topic, the Cegedim Insurance Solutions team is at your disposal to answer all your questions.